Nigeria is one of the countries with the largest adolescent population; over 60 million. Adolescence is a crucial period as youths transition into adults. However, there are certain health problems that many of these young adults are faced with.
This article aims to pinpoint some of the common adolescent health problems in Nigeria, their effects, causes and practical solutions to mitigate or eradicate these pertinent issues.
5 COMMON ADOLESCENT HEALTH PROBLEMS IN NIGERIA

These adolescent health problems in Nigeria include health issues that are commonly faced by adolescents in Nigeria. Adolescents age ranges from 13-19 years. [1]
1. Alcohol and Drugs abuse
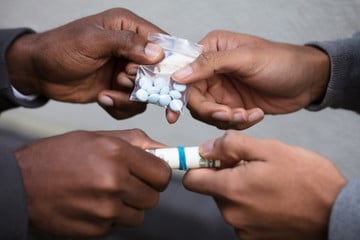
Drug abuse is the use of certain chemicals or substances for the purpose of creating pleasurable effects on the brain.
Alcohol and Drugs abuse has grown to become one of the leading adolescent health problems in Nigeria. In fact, a recent statistics released by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime and the European Union a few months ago revealed that about 14.3 million or 14.4 percent Nigerians abuse drugs annually. [2]
According to reports, the commonly abused drugs in Nigeria include cocaine, heroin, amphetamines, Indian hemp, tramadol, codeine, cough syrup, laxatives, and the host of others.
Reports like this ought to be very worrisome to the government and other relevant agencies, especially when considering the harmful effects drug or substance abuse pose on both the people who are into it and the society at large.
Effects of Drug abuse:
- Family breakdown
- Increased rape and women abuse
- Increased crime rate
- Sudden increase in the population of patients at rehabilitation centers
- Weakened immune system
- Heart attacks
- Lung disease
- Lowered mental function
- Increased strain on the liver and Liver damage or failure
- Decreased interest in others
- Impaired judgment
- Change in personality
Causes:
- Social influence
- Curiosity and experimentation
- Lack of parental care
- Frustration or feeling of being isolated
- Peer pressure among young adults
- Boredom and Idleness
- Co-occurring disorders, such as depression and anxiety
- Lack of adequate information or enlightenment about the consequences of drug abuse
Practical Solutions:
- Parents should adequately monitor their kids and the friends they interact with.
- The Government and other relevant agencies should extinct all the sources of hard substances in the nation.
- Schools should educate their students on the negative effects of drug abuse.
- Relevant authorities should come up with continuous campaign against the use of hard substances. This could be done both via the traditional media houses and online platforms with a high population of young folks.
- The government should make sure that every offender is made to face the wrath of the law when caught in any drug-abuse related activity.
- Rehabilitation centers should be established for the purpose of rehabilitating and transforming drug abusers. They are many other effective ways to prevent drug abuse in Nigeria.
2. Physical Injuries and disability
In Nigeria, people with disabilities and certain injuries keep increasing day by day, with women and children topping the chart.
Hardly will you go to any street in the nation without seeing people with this challenge, showing that it’s a national issue worthy of utmost concern. [3]
Although there are a number of reasons for disability in Nigeria, the foremost is Road Traffic Accident, which is responsible for thousands of trauma-related deaths annually.
Again, it might interest you to know that most of the factors that lead to disabilities are preventable, at least to a significant extent.
Effects:
Physical disability has created lots of worrisome effects both in the concerned people and Nigeria at large.
People with disabilities are often undermined and are denied access to a number of things, including elementary education, public transportation, buildings, social and cultural life, and the likes.
In addition to that, the vast majority disabled in Nigeria also suffer discrimination, stigmatization, exclusion and neglect of their special needs, which is completely against humanity.
A lot of them have great and innovative minds, but they are rarely employed in our companies, private firms, public sectors – all because of their physical state.
Again, since the relevant authorities and the family of people with disabilities seldom uphold their rights, they often resort to street begging, which further exposes them to more risks – automobile accident, kidnap, abuse, etc.
More importantly, studies reveal that children and women are three times more susceptible to physical, sexual and economic abuse. In fact, the vast majority of them are denied access to basic education and marriage.
Causes:
- Common causes of disability in Nigeria include but not limited to –
- Road Traffic Accident
- Conflicts and violence
- Mishandling of sophisticated machineries at workplace
- Exposure to extremely harmful chemicals at the workplace
Practical Solutions:
The Government, through the Ministry of Women Affairs and Social Development Goals, should launch special education, social welfare and health services targeted at people with disabilities.
The government should also come up with programs for protecting the rights of people with disabilities.
Business enterprises should employ people with disabilities, provided their physical state has nothing to do with the job.
Political parties in the nation should encourage people with disabilities by giving them the right to contest for any post in their party.
The government and other relevant bodies should put in place disability-friendly systems for the disabled.
Schools should incorporate subjects and courses that promote social inclusion in their curriculum.
The government and independent bodies should organize scholarships and awards for people with disabilities.
The government should ensure that all the available means of transportation are universally accessible for its citizens, including people with certain disabilities.
Social institutions like religious houses should let their followers realize that people with disabilities are humans too.
The government, through the Federal Road Safety Corps [FRSC] and other relevant agencies, should ensure that the vehicles and roads are safe to prevent road traffic accident, the common cause of disability in the nation.
Factories with sophisticated and powerful machinery/tools should ensure that their workers are well protected simply by putting in place the necessary safety measures.
3. Mental Disorders

Mental disorder is yet another pressing adolescent health problem in Nigeria. Report shows that an estimated 20% – 30% or about 60 million Nigerians are suffering from mental disorders.
Mental disorder refers to any health condition that results in a negative change of emotion, mood, thinking or behavior [or the combination].
Common mental health problems in Nigeria include ADHD, dementia, bipolar affective disorder, schizophrenia, anxiety disorders, anorexia nervosa, and depression.
The unfortunate thing is that the attention given to mental health problem in Nigeria isn’t adequate, and also the level of awareness of the populace as regards mental issues is quite low.
That said, it will interest you to know that only 3.3% of Nigeria’s total health budget is allocated to mental health, which accounts for the reason why we have only a few number of health professionals in our public system. You can take look at the shocking mental health statistics in Nigeria.
Effects/symptoms:
- Withdrawal from friends and activities
- Changes in mood
- Declined mental function and concentration
- Confused thinking
- Inability to cope with daily issues or stress
- Decline in performance at the workplace
- Suicidal thinking
- Sudden change in behavior
Causes:
- Genetics [heredity]
- Brain defects or injury
- Changes in neurotransmitters
- Stressful life events
- Certain infection, such as Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorder [PANDA].
- Traumatic events
- Prenatal damage, i.e. a trauma or disruption of early fetal brain development.
- Drugs or substance abuse
- Sudden loss of a loved one
- Neglect
Practical Solutions:
The government and other relevant bodies should undertake the widespread education of the populace on the major causes of mental disorder and prevention tips.
Individuals should offer support and encouragement to people with mental disorder instead of stigmatizing or neglecting them.
The government should allocate enough funds to mental health to significantly reduce the condition in the country.
People with mental disorders should be taken to a qualified mental health professional rather than isolating them.
The government should restrict access to hard drugs and ensure that offenders are duly penalized.
Pregnant moms should avoid any activity that can trigger Prenatal damage, i.e. trauma or disruption of early fetal brain development.
Expectant mothers should avoid taking hard drugs or substances as it can make their unborn child more susceptible to certain mental disorders.
4. Teenage pregnancy and childbirth

Teenage pregnancy is when a female adolescent becomes pregnant or bears child between the ages of 13 – 19.
Teenage pregnancy and childbirth is again another trending adolescent health problem in Nigeria. In fact, it now a major adolescent reproductive health issue in Nigeria.
Research shows that 23 percent of women aged 15-19 years have begun childbearing, of which 5% are pregnant with their first child.
Furthermore, below is a statistical figure showing how different geopolitical zones in Nigerian stand in regards to Teenage pregnancy and childbirth: [4]
- Northwest (36%)
- Northeast (32%)
- North Central (19%)
- South Central (12%)
- Southeast (8%)
- Southwest (8%)
From the above statistics, it can be deduced that there is a direct relationship between early pregnancy, literacy levels and poverty. For instance, the northern region with the lowest literacy rates and highest poverty rates has the biggest prevalence of early pregnancy.
Early pregnancy could have been a thing of the past or reduced by a significant in Nigeria, but it is very unfortunate that comprehensive sex education is not prioritized, unlike in advanced countries where their teenagers are well informed about sex.
In fact, advocates of sex education suffer intense resistance from religious leaders as they believe that teachings like this will promote immorality in the society and corrupt the mind of the young ones.
Effects:
The dangers associated with early pregnancy and childbirth can never be overemphasized as it has led to a number of wreckage in the nation.
The vast majority of young girls with early pregnancy are often withdrawn from school, denied of further education, tied to a partner they don’t like in a real sense, languish in poverty, struggle with certain health issues, and the host of others.
Additionally, studies reveal that the girl’s young bodies cannot cope with the stress associated with pregnancy and child labour, therefore exposing the mother and her baby to serious health conditions or even death.
That said, it is equally important to let you to know that rates of stillbirth, pre-term birth, low body weight, suffocation, and death of newborns in mothers below age 20 are 50% higher than the analogical rates of mothers who are above that age bracket.
That’s not all; getting pregnant at a very tender age can result to a number of health conditions, including HIV/AIDS, malaria, anemia, mental disorders, Sexually-Transmitted Diseases [STDs], postpartum hemorrhage, to name but a few. Again, thousands of young teenagers reportedly die or develop a permanent sexual disability as a result of a failed abortion.
Causes:
- Unprotected sex
- Poverty and illiteracy i.e. lack of education
- Rape
- Changes in societal values
- Victimization
- Sexual abuse and violence
- Cultural and religious traditions
- Unawareness of personal rights
- Ignorance
- Lack of special establishments for teen rights protection
Practical Solutions:
- Comprehensive sex education should be given to teenagers
- The government and other relevant bodies should organize reproductive health services for youngsters.
- Non-Governmental Organizations [NGOs] should always sensitize teenage mothers-to-be on the need to access health care to reduce the complications linked with early pregnancy.
- NGOs and the government should ensure that young mothers get antenatal and postnatal care.
- The government should curb rape, the common cause of early pregnancy by ensuring that rapists are punished by the law.
- The judiciary arm of the government should deliver accurate, unbiased, timely judgment for rape and other sexual-abuse related cases.
- Schools should ensure that lecturers or teachers who victimize young girls do not go unpunished.
- Business owners should enact a bylaw that punishes rapists or sexual abusers.
- Civil society groups, policymakers and other relevant bodies should form a campaign to fight and put an end to teenage pregnancy.
- Teenagers should be taught what contraceptives are, their uses, and how to use them.
- Contraceptives should be made available and accessible across the nation at reasonable prices.
- The custom of early marriages should be forgotten, and young teenagers should be allowed to make marital decisions only when they are mature enough.
- Parents should love and take care of their kids, talk to them, explain any questions that may be bothering their mind.
- There should be a firm and effective adolescent health policy in Nigeria.
5. HIV/AIDS
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a virus that damages the immune system [the body’s defense mechanism that shields against infections and other invaders].
It can be transmitted via bodily fluids, including blood, semen, vaginal/rectal fluids, breast milk, etc.
When left untreated, people with this lifelong condition can further develop AIDS, which could shorten their life span.
Nigeria has an estimated 1.9 million (1.5%) people living with HIV, making it one of the countries with the highest HIV prevalence.
The country is also said to account for nearly half of all new HIV infections in Sub-Saharan Africa annually.
Based on reports, the south-south zone of Nigeria has the highest prevalence of this virus, at 3.1 percent, closely followed by North Central Zone (2.0%), South East Zone (1.9%), South West Zone (1.1%), North East Zone (1. 1%) while Northwest zone has the lowest prevalence, at 0.6% among adults aged 15 – 49 years. The top states include Akwa Ibom, Benue, Rivers, Taraba, Cross River and Enugu. [5]
That said, it might interest you to know that some categories of people are more prone to HIV than the other in Nigeria. This includes women (58% of the people living with HIV are women), children and orphans, young people, people who inject drugs (PWID), sexual workers, gay, among others.
Effects:
- Increased proportion of indoor patients
- Decreased family revenue
- Increased expenditure for treatment
- Loss of job
- People with the virus often suffer stigmatization, discrimination, and isolation.
Causes:
- Having Unprotected sex [sex without a condom] with someone who has HIV.
- Sharing needles, syringes and other equipment used for injecting drugs.
- Blood transfusion
- Mother-to-child transmission; during pregnancy, childbirth or breastfeeding
Practical Solutions:
- The Government should increase access to treatment for people living with HIV.
- People who are tested positive for HIV should be referred to treatment facilities immediately they are diagnosed with the virus.
- People with HIV/AIDS should be given adequate care and support to curb AIDS-related stigma.
- The government should develop a more effective plan that oversees the better provision of HIV prevention, care and treatment services.
- Individuals should practice safe sex by using a new condom whenever they want to have sex.
- Individuals should avoid sharing needles, syringes or other sharp equipment.
- Individuals should Avoid piercing and tattooing. However, if you must do either of the two, be sure to get it done at a licensed studio where all the equipment used are properly sterilized.
- Mothers with HIV should avoid breastfeeding their babies to avoid transmission.
- Relevant authorities should come up with continuous campaign against early pregnancy and childbirth.
- Sex education should be prioritized in our schools, religious houses, and other socialization agents.
Bottom Line
Young people in Nigeria suffer from numerous health challenges. These adolescent health problems in Nigeria discussed above should give you insight into what they are facing, and the solutions should motivate you to work toward solving them.
Thanks for reading. Please share and leave a comment.



